
Before you begin
- Labs create a Google Cloud project and resources for a fixed time
- Labs have a time limit and no pause feature. If you end the lab, you'll have to restart from the beginning.
- On the top left of your screen, click Start lab to begin
Install ADK and set up your environment
/ 50
Create API key and deploy ADK agent
/ 50
In this lab, you will explore Model Context Protocol (MCP), an open standard that enables seamless integration between external services, data sources, tools, and applications. You will learn how to integrate MCP into your ADK agents, using tools provided by existing MCP servers to enhance your ADK workflows. Additionally, you will see how to expose ADK tools like load_web_page through a custom-built MCP server, enabling broader integration with MCP clients.
What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard designed to standardize how Large Language Models (LLMs) like Gemini and Claude communicate with external applications, data sources, and tools. Think of it as a universal connection mechanism that simplifies how LLMs obtain context, execute actions, and interact with various systems.
MCP follows a client-server architecture, defining how data (resources), interactive templates (prompts), and actionable functions (tools) are exposed by an MCP server and consumed by an MCP client (which could be an LLM host application or an AI agent).
This lab covers two primary integration patterns:
In this lab, you learn how to:
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This Qwiklabs hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
Note: If you already have your own personal Google Cloud account or project, do not use it for this lab.
Note: If you are using a Pixelbook, open an Incognito window to run this lab.
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a dialog opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details pane with the following:
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
You can also find the Username in the Lab Details pane.
Click Next.
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
You can also find the Password in the Lab Details pane.
Click Next.
Click through the subsequent pages:
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

In this lab environment, the Vertex AI API, Routes API and Directions API have been enabled for you.
With your Google Cloud console window selected, open Cloud Shell by pressing the G key and then the S key on your keyboard. Alternatively, you can click the Activate Cloud Shell button (
Click Continue.
When prompted to authorize Cloud Shell, click Authorize.
In the upper right corner of the Cloud Shell Terminal panel, click the Open in new window button 
In the Cloud Shell Terminal, enter the following to open the Cloud Shell Editor to your home directory:
Close any additional tutorial or Gemini panels that appear on the right side of the screen to save more of your window for your code editor.
Throughout the rest of this lab, you can work in this window as your IDE with the Cloud Shell Editor and Cloud Shell Terminal.
Install ADK by running the following command in the Cloud Shell Terminal.
Paste the following commands into the Cloud Shell Terminal to copy a file from a Cloud Storage bucket, and unzip it, creating a project directory with code for this lab:
Install additional lab requirements with:
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
This section demonstrates how to integrate tools from an external Google Maps MCP server into your ADK agents. This is the most common integration pattern when your ADK agent needs to use capabilities provided by an existing service that exposes an MCP interface. You will see how the MCPToolset class can be directly added to your agent's tools list, enabling seamless connection to an MCP server, discovery of its tools, and making them available for your agent to use. These examples primarily focus on interactions within the adk web development environment.
The MCPToolset class is ADK's primary mechanism for integrating tools from an MCP server. When you include an MCPToolset instance in your agent's tools list, it automatically handles the interaction with the specified MCP server. Here's how it works:
MCPToolset establishes and manages the connection to the MCP server. This can be a local server process (using StdioServerParameters for communication over standard input/output) or a remote server (using SseServerParams for Server-Sent Events). The toolset also handles the graceful shutdown of this connection when the agent or application terminates.MCPToolset queries the MCP server for its available tools (via the list_tools MCP method). It then converts the schemas of these discovered MCP tools into ADK-compatible BaseTool instances.LlmAgent as if they were native ADK tools.LlmAgent decides to use one of these tools, MCPToolset transparently proxies the call (using the call_tool MCP method) to the MCP server, sends the necessary arguments, and returns the server's response back to the agent.tool_filter parameter when creating an MCPToolset to select a specific subset of tools from the MCP server, rather than exposing all of them to your agent.In this sub-section, you will generate a new API key named GOOGLE_MAPS_API_KEY.
Open the browser tab displaying the Google Cloud Console (not your Cloud Shell Editor).
You can close the Cloud Shell Terminal pane on this browser tab for more console area.
Search for Credentials in the search bar at the top of the page. Select it from the results.
On the Credentials page, click + Create Credentials at the top of the page, then select API key.
The API key created dialog will display your newly created API key. Be sure to save this key locally for later use in the lab.
Click Close on the dialog box.
Your newly created key will be named API Key 1 by default. Select the key, rename it to GOOGLE_MAPS_API_KEY, and click Save.
In this sub-section, you will configure your agent to use the MCPToolset for Google Maps, enabling it to seamlessly provide directions and location-based information.
In the Cloud Shell Editor's file explorer pane, find the adk_mcp_tools folder. Click it to toggle it open.
Navigate to the directory adk_mcp_tools/google_maps_mcp_agent.
Paste the following command in a plain text file, then update the YOUR_ACTUAL_API_KEY value with the Google Maps API key you generated and saved in a previous step:
Copy and paste the updated command to Cloud Shell Terminal to run it and write a .env file which will provide authentication details for this agent directory.
Copy the .env file to the other agent directory you will use in this lab by running the following command:
Next, add the following code where indicated in the agent.py file to add the Google maps tool to your agent. This will allow your agent to use the MCPToolset for Google Maps to provide directions or location-based information.
From the adk_mcp_tools project directory, launch the Agent Development Kit Dev UI with the following command:
Output:
To view the web interface in a new tab, click the http://127.0.0.1:8000 link in the Terminal output.
A new browser tab will open with the ADK Dev UI. From the Select an agent dropdown on the left, select the google_maps_mcp_agent from the dropdown.
Start a conversation with the agent and run the following prompts:
Output:
Click the agent icon next to the agent's chat bubble with a lightning bolt, which indicates a function call. This will open up the Event inspector for this event:
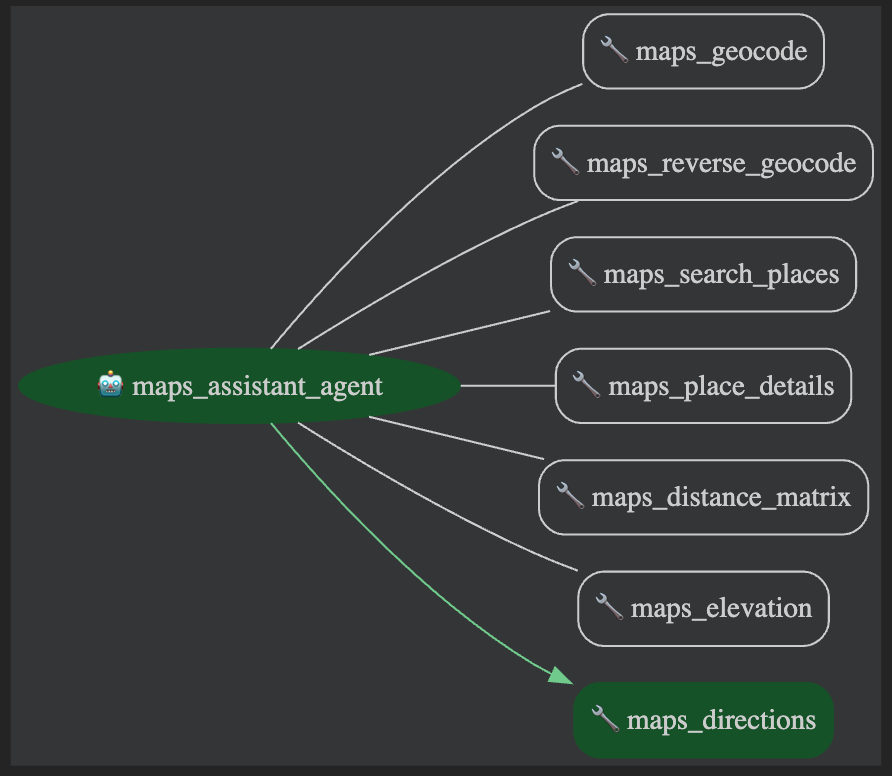
Notice that agent graph indicates several different tools, identified by the wrench emoji (🔧). Even though you only imported one MCPToolset, that tool set came with the different tools you see listed here, such as maps_place_details and maps_directions.
On the Request tab, you can see the structure of the request. You can use the arrows at the top of the Event inspector to browse the agent's thoughts, function calls, and responses.
When you are finished asking questions of this agent, close the dev UI browser tab.
Go back to the Cloud Shell Terminal panel and press CTRL + C to stop the server.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
In this section, you'll learn how to expose the ADK load_web_page tool through a custom-built MCP server. This pattern allows you to wrap existing ADK tools and make them accessible to any standard MCP client application.
Return to your Cloud Shell Editor tab and select the adk_mcp_tools/adk_mcp_server directory.
A Python file named adk_server.py has been prepared and commented for you. Take some time to review that file, reading the comments to understand how the code wraps a tool and serves it as an MCP server. Notice how it allows MCP clients to list available tools as well as invoke the ADK tool asynchronously, handling requests and responses in an MCP-compliant format.
Click on the agent.py file in the adk_mcp_server directory.
Update the path to your adk_server.py file.
Next, add the following code where indicated in the agent.py file to add the MCPToolset to your agent. An ADK agent acts as a client to the MCP server. This ADK agent will use MCPToolset to connect to your adk_server.py script.
To run the MCP server, start the adk_server.py script by running the following command in Cloud Shell Terminal:
Output:
Open a new Cloud Shell Terminal tab by clicking the 
In the Cloud Shell Terminal, from the adk_mcp_tools project directory, launch the Agent Development Kit Dev UI with the following command:
To view the web interface in a new tab, click the http://127.0.0.1:8000 link in the Terminal output.
From the Select an agent dropdown on the left, select the adk_mcp_server from the dropdown.
Query the agent with:
Output:
What happens here:
web_reader_mcp_client_agent) uses the MCPToolset to connect to your adk_server.py.call_tool request, execute the ADK load_web_page tool, and return the result.adk_server.py terminal in the Cloud Shell Terminal tab where it is running.This demonstrates that ADK tools can be encapsulated within an MCP server, making them accessible to a broad range of MCP-compliant clients including ADK agents.
At the end of this lab, you have learned how to integrate external Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools into your ADK agents using the MCPToolset class. You’ve discovered how to connect to an MCP server, use its tools within your agent, and expose ADK tools like load_web_page through a custom MCP server. These skills enable you to extend your ADK agents with powerful, external services, enhancing your web development workflows.
Manual Last Updated October 6, 2025
Lab Last Tested October 6, 2025
Copyright 2023 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.




This content is not currently available
We will notify you via email when it becomes available

Great!
We will contact you via email if it becomes available


One lab at a time
Confirm to end all existing labs and start this one
