GSP903

概览
Google Cloud Pub/Sub 是一项用于在应用和服务之间交换事件数据的消息传递服务。数据生产者会将消息发布到 Cloud Pub/Sub 主题。使用方可以为该主题创建订阅。订阅方既可以从订阅中拉取消息,也可以配置 Webhook 端点以接收推送订阅。每个订阅方都必须在可配置的时间窗口内确认每条消息。
Dataflow 是一种全托管式服务,可在流式(实时)模式和批量模式下对数据进行转换和丰富,且在两种模式下具备同等的可靠性与表达能力。它借助 Apache Beam SDK 提供了简化的流水线开发环境。Apache Beam SDK 具备丰富的窗口化与会话分析原语,并拥有完善的源与汇连接器生态系统。
Pub/Sub 是一个可扩展且持久的事件摄取与传送系统。在使用窗口和缓冲功能时,Dataflow 的消息去重和“仅传送一次”的按序处理能力,与 Pub/Sub 可扩展的“至少一次”传送模型形成互补。
您将执行的操作
- 读取发布到 Pub/Sub 主题的消息
- 按时间戳对消息进行窗口化(或分组)
- 将消息写入 Cloud Storage
设置
点击“开始实验”按钮前的注意事项
请阅读以下说明。实验是计时的,并且您无法暂停实验。计时器在您点击开始实验后即开始计时,显示 Google Cloud 资源可供您使用多长时间。
此实操实验可让您在真实的云环境中开展实验活动,免受模拟或演示环境的局限。为此,我们会向您提供新的临时凭据,您可以在该实验的规定时间内通过此凭据登录和访问 Google Cloud。
为完成此实验,您需要:
- 能够使用标准的互联网浏览器(建议使用 Chrome 浏览器)。
注意:请使用无痕模式(推荐)或无痕浏览器窗口运行此实验。这可以避免您的个人账号与学生账号之间发生冲突,这种冲突可能导致您的个人账号产生额外费用。
注意:请仅使用学生账号完成本实验。如果您使用其他 Google Cloud 账号,则可能会向该账号收取费用。
如何开始实验并登录 Google Cloud 控制台
-
点击开始实验按钮。如果该实验需要付费,系统会打开一个对话框供您选择支付方式。左侧是“实验详细信息”窗格,其中包含以下各项:
- “打开 Google Cloud 控制台”按钮
- 剩余时间
- 进行该实验时必须使用的临时凭据
- 帮助您逐步完成本实验所需的其他信息(如果需要)
-
点击打开 Google Cloud 控制台(如果您使用的是 Chrome 浏览器,请右键点击并选择在无痕式窗口中打开链接)。
该实验会启动资源并打开另一个标签页,显示“登录”页面。
提示:将这些标签页安排在不同的窗口中,并排显示。
注意:如果您看见选择账号对话框,请点击使用其他账号。
-
如有必要,请复制下方的用户名,然后将其粘贴到登录对话框中。
{{{user_0.username | "<用户名>"}}}
您也可以在“实验详细信息”窗格中找到“用户名”。
-
点击下一步。
-
复制下面的密码,然后将其粘贴到欢迎对话框中。
{{{user_0.password | "<密码>"}}}
您也可以在“实验详细信息”窗格中找到“密码”。
-
点击下一步。
重要提示:您必须使用实验提供的凭据。请勿使用您的 Google Cloud 账号凭据。
注意:在本实验中使用您自己的 Google Cloud 账号可能会产生额外费用。
-
继续在后续页面中点击以完成相应操作:
- 接受条款及条件。
- 由于这是临时账号,请勿添加账号恢复选项或双重验证。
- 请勿注册免费试用。
片刻之后,系统会在此标签页中打开 Google Cloud 控制台。
注意:如需访问 Google Cloud 产品和服务,请点击导航菜单,或在搜索字段中输入服务或产品的名称。

激活 Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell 是一种装有开发者工具的虚拟机。它提供了一个永久性的 5GB 主目录,并且在 Google Cloud 上运行。Cloud Shell 提供可用于访问您的 Google Cloud 资源的命令行工具。
-
点击 Google Cloud 控制台顶部的激活 Cloud Shell  。
。
-
在弹出的窗口中执行以下操作:
- 继续完成 Cloud Shell 信息窗口中的设置。
- 授权 Cloud Shell 使用您的凭据进行 Google Cloud API 调用。
如果您连接成功,即表示您已通过身份验证,且项目 ID 会被设为您的 Project_ID 。输出内容中有一行说明了此会话的 Project_ID:
Your Cloud Platform project in this session is set to {{{project_0.project_id | "PROJECT_ID"}}}
gcloud 是 Google Cloud 的命令行工具。它已预先安装在 Cloud Shell 上,且支持 Tab 自动补全功能。
- (可选)您可以通过此命令列出活跃账号名称:
gcloud auth list
- 点击授权。
输出:
ACTIVE: *
ACCOUNT: {{{user_0.username | "ACCOUNT"}}}
To set the active account, run:
$ gcloud config set account `ACCOUNT`
- (可选)您可以通过此命令列出项目 ID:
gcloud config list project
输出:
[core]
project = {{{project_0.project_id | "PROJECT_ID"}}}
注意:如需查看在 Google Cloud 中使用 gcloud 的完整文档,请参阅 gcloud CLI 概览指南。
设置区域
- 在 Cloud Shell 中,运行以下命令,设置本实验的项目区域:
gcloud config set compute/region {{{project_0.default_region | "REGION"}}}
确保 Dataflow API 已成功启用
为确保可以访问所需的 API,请重新启动与 Dataflow API 的连接。
gcloud services disable dataflow.googleapis.com --project {{{project_0.project_id|Project ID}}} --force
gcloud services enable dataflow.googleapis.com --project {{{project_0.project_id|Project ID}}}
点击检查我的进度以验证是否完成了以下目标:
停用并重新启用 Dataflow API
任务 1. 创建项目资源
- 在 Cloud Shell 中,为您的存储桶、项目和区域创建变量。
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
BUCKET_NAME="${PROJECT_ID}-bucket"
TOPIC_ID=my-id
REGION={{{project_0.default_region | "filled in at lab start"}}}
- 设置 App Engine 区域。
注意:对于 us-central1 和 europe-west1 以外的区域,请将 App Engine 区域变量设置为与分配的区域相同。如果您被分配到 us-central1,请将 App Engine 区域变量设置为 us-central。如果您被分配到 europe-west1,请将 App Engine 区域变量设置为 europe-west。
如需了解详情,请参阅 App Engine 位置。
AE_REGION={{{project_0.startup_script.app_region|region_to_be_set}}}
- 创建此项目所拥有的 Cloud Storage 存储桶:
gsutil mb gs://$BUCKET_NAME
注意:Cloud Storage 存储桶名称必须全局唯一。您的 Qwiklabs 项目 ID 始终唯一,因此本实验在存储桶名称中使用了项目 ID。
- 在此项目中创建 Pub/Sub 主题:
gcloud pubsub topics create $TOPIC_ID
- 为您的项目创建 App Engine 应用:
gcloud app create --region=$AE_REGION
- 在此项目中创建 Cloud Scheduler 作业。该作业每隔 1 分钟向 Cloud Pub/Sub 主题发布一条消息:
gcloud scheduler jobs create pubsub publisher-job --schedule="* * * * *" \
--topic=$TOPIC_ID --message-body="Hello!"
- 如果系统提示您启用 Cloud Scheduler API,请按
y 并按 Enter 键。
点击检查我的进度以验证是否完成了以下目标:
创建项目资源
- 启动作业:
gcloud scheduler jobs run publisher-job
注意:如果您遇到 RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED 错误,请再次尝试执行该命令。
- 使用以下命令克隆快速入门代码库并前往示例代码目录:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/java-docs-samples.git
cd java-docs-samples/pubsub/streaming-analytics
docker run -it -e DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID=$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID python:3.7 /bin/bash
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/python-docs-samples.git
cd python-docs-samples/pubsub/streaming-analytics
pip install -U -r requirements.txt # 安装 Apache Beam 依赖项
注意:如果您使用 Python 选项,请单独逐条执行 Python 命令。
点击检查我的进度以验证是否完成了以下目标:
启动 Cloud Scheduler 作业
任务 2. 查看将消息从 Pub/Sub 流式传输到 Cloud Storage 的代码
代码示例
查看以下示例代码,该代码使用 Dataflow 执行以下操作:
- 读取 Pub/Sub 消息。
- 按发布时间戳对消息进行窗口化(或分组),并按固定时间间隔处理。
- 将每个窗口中的消息写入 Cloud Storage 中的文件。
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.beam.examples.common.WriteOneFilePerWindow;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.Pipeline;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.io.gcp.pubsub.PubsubIO;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.options.Default;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.options.Description;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.options.PipelineOptionsFactory;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.options.StreamingOptions;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.options.Validation.Required;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.transforms.windowing.FixedWindows;
import org.apache.beam.sdk.transforms.windowing.Window;
import org.joda.time.Duration;
public class PubSubToGcs {
/*
* Define your own configuration options. Add your own arguments to be processed
* by the command-line parser, and specify default values for them.
*/
public interface PubSubToGcsOptions extends StreamingOptions {
@Description("The Cloud Pub/Sub topic to read from.")
@Required
String getInputTopic();
void setInputTopic(String value);
@Description("Output file's window size in number of minutes.")
@Default.Integer(1)
Integer getWindowSize();
void setWindowSize(Integer value);
@Description("Path of the output file including its filename prefix.")
@Required
String getOutput();
void setOutput(String value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// The maximum number of shards when writing output.
int numShards = 1;
PubSubToGcsOptions options =
PipelineOptionsFactory.fromArgs(args).withValidation().as(PubSubToGcsOptions.class);
options.setStreaming(true);
Pipeline pipeline = Pipeline.create(options);
pipeline
// 1) Read string messages from a Pub/Sub topic.
.apply("Read PubSub Messages", PubsubIO.readStrings().fromTopic(options.getInputTopic()))
// 2) Group the messages into fixed-sized minute intervals.
.apply(Window.into(FixedWindows.of(Duration.standardMinutes(options.getWindowSize()))))
// 3) Write one file to GCS for every window of messages.
.apply("Write Files to GCS", new WriteOneFilePerWindow(options.getOutput(), numShards));
// Execute the pipeline and wait until it finishes running.
pipeline.run().waitUntilFinish();
}
}
import argparse
from datetime import datetime
import logging
import random
from apache_beam import (
DoFn,
GroupByKey,
io,
ParDo,
Pipeline,
PTransform,
WindowInto,
WithKeys,
)
from apache_beam.options.pipeline_options import PipelineOptions
from apache_beam.transforms.window import FixedWindows
class GroupMessagesByFixedWindows(PTransform):
"""A composite transform that groups Pub/Sub messages based on publish time
and outputs a list of tuples, each containing a message and its publish time.
"""
def __init__(self, window_size, num_shards=5):
# Set window size to 60 seconds.
self.window_size = int(window_size * 60)
self.num_shards = num_shards
def expand(self, pcoll):
return (
pcoll
# Bind window info to each element using element timestamp (or publish time).
| "Window into fixed intervals"
>> WindowInto(FixedWindows(self.window_size))
| "Add timestamp to windowed elements" >> ParDo(AddTimestamp())
# Assign a random key to each windowed element based on the number of shards.
| "Add key" >> WithKeys(lambda _: random.randint(0, self.num_shards - 1))
# Group windowed elements by key. All the elements in the same window must fit
# memory for this. If not, you need to use `beam.util.BatchElements`.
| "Group by key" >> GroupByKey()
)
class AddTimestamp(DoFn):
def process(self, element, publish_time=DoFn.TimestampParam):
"""Processes each windowed element by extracting the message body and its
publish time into a tuple.
"""
yield (
element.decode("utf-8"),
datetime.utcfromtimestamp(float(publish_time)).strftime(
"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f"
),
)
class WriteToGCS(DoFn):
def __init__(self, output_path):
self.output_path = output_path
def process(self, key_value, window=DoFn.WindowParam):
"""Write messages in a batch to Google Cloud Storage."""
ts_format = "%H:%M"
window_start = window.start.to_utc_datetime().strftime(ts_format)
window_end = window.end.to_utc_datetime().strftime(ts_format)
shard_id, batch = key_value
filename = "-".join([self.output_path, window_start, window_end, str(shard_id)])
with io.gcsio.GcsIO().open(filename=filename, mode="w") as f:
for message_body, publish_time in batch:
f.write(f"{message_body},{publish_time}\n".encode())
def run(input_topic, output_path, window_size=1.0, num_shards=5, pipeline_args=None):
# Set `save_main_session` to True so DoFns can access globally imported modules.
pipeline_options = PipelineOptions(
pipeline_args, streaming=True, save_main_session=True
)
with Pipeline(options=pipeline_options) as pipeline:
(
pipeline
# Because `timestamp_attribute` is unspecified in `ReadFromPubSub`, Beam
# binds the publish time returned by the Pub/Sub server for each message
# to the element's timestamp parameter, accessible via `DoFn.TimestampParam`.
# https://beam.apache.org/releases/pydoc/current/apache_beam.io.gcp.pubsub.html#apache_beam.io.gcp.pubsub.ReadFromPubSub
| "Read from Pub/Sub" >> io.ReadFromPubSub(topic=input_topic)
| "Window into" >> GroupMessagesByFixedWindows(window_size, num_shards)
| "Write to GCS" >> ParDo(WriteToGCS(output_path))
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.INFO)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--input_topic",
help="The Cloud Pub/Sub topic to read from."
'"projects//topics/".',
)
parser.add_argument(
"--window_size",
type=float,
default=1.0,
help="Output file's window size in minutes.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--output_path",
help="Path of the output GCS file including the prefix.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--num_shards",
type=int,
default=5,
help="Number of shards to use when writing windowed elements to GCS.",
)
known_args, pipeline_args = parser.parse_known_args()
run(
known_args.input_topic,
known_args.output_path,
known_args.window_size,
known_args.num_shards,
pipeline_args,
)
注意:如需进一步了解示例代码,请访问相应的 java-docs-samples 和 python-docs-samples GitHub 页面。
任务 3. 启动流水线
- 如需启动流水线,请运行以下命令:
mvn compile exec:java \
-Dexec.mainClass=com.examples.pubsub.streaming.PubSubToGcs \
-Dexec.cleanupDaemonThreads=false \
-Dexec.args=" \
--project=$PROJECT_ID \
--region=$REGION \
--inputTopic=projects/$PROJECT_ID/topics/$TOPIC_ID \
--output=gs://$BUCKET_NAME/samples/output \
--runner=DataflowRunner \
--windowSize=2 \
--tempLocation=gs://$BUCKET_NAME/temp"
python PubSubToGCS.py \
--project=project_id \
--region=region \
--input_topic=projects/project_id/topics/my-id \
--output_path=gs://bucket_name/samples/output \
--runner=DataflowRunner \
--window_size=2 \
--num_shards=2 \
--temp_location=gs://bucket_name/temp
注意:执行 Python 命令时,请将 project_id、bucket_name 和 region 分别替换为您的项目 ID、存储桶名称和分配的实验区域。
上述命令在本地运行,并在云端启动一个 Dataflow 作业。
注意:您可能需要等待大约 10 分钟,代码才能彻底执行完毕,随后您将在下一任务中于 Dataflow 控制台看到该流水线作业。
注意:如果您收到与 StaticLoggerBinder 相关的警告,可以放心忽略,继续实验。
点击检查我的进度以验证是否完成了以下目标:
启动流水线并启动 Dataflow 作业
任务 4. 查看作业和流水线进度
-
前往 Dataflow 控制台查看作业进度。
-
点击刷新以查看作业及其最新状态更新。
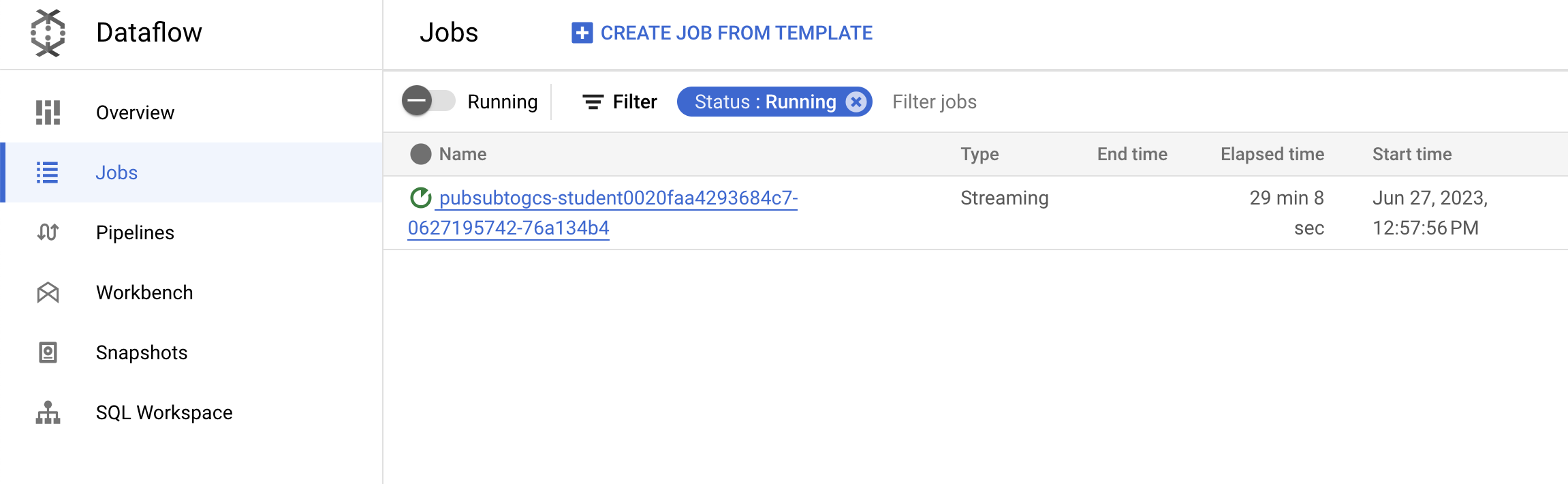
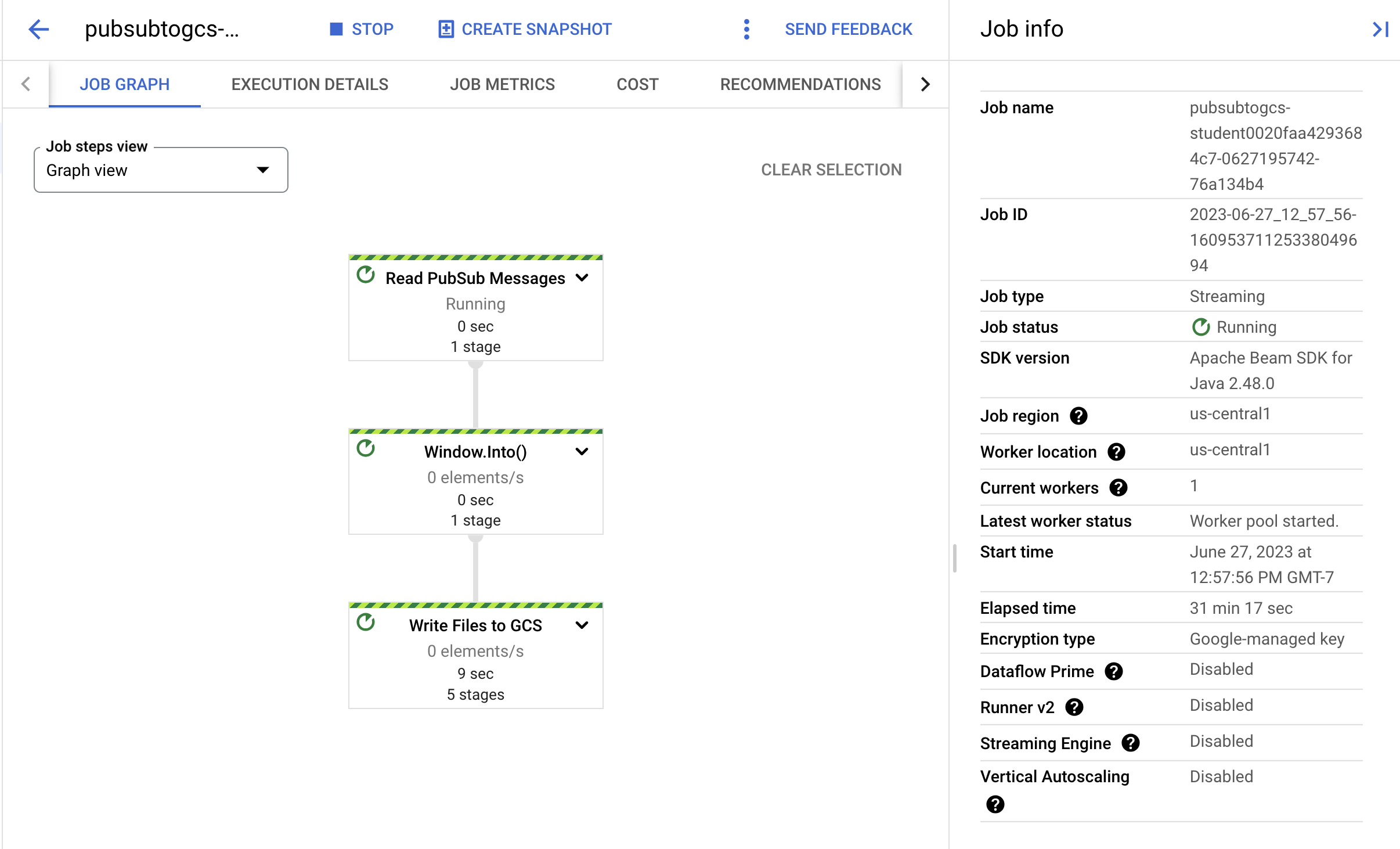
- 点击作业名称以打开作业详细信息,并查看以下内容:
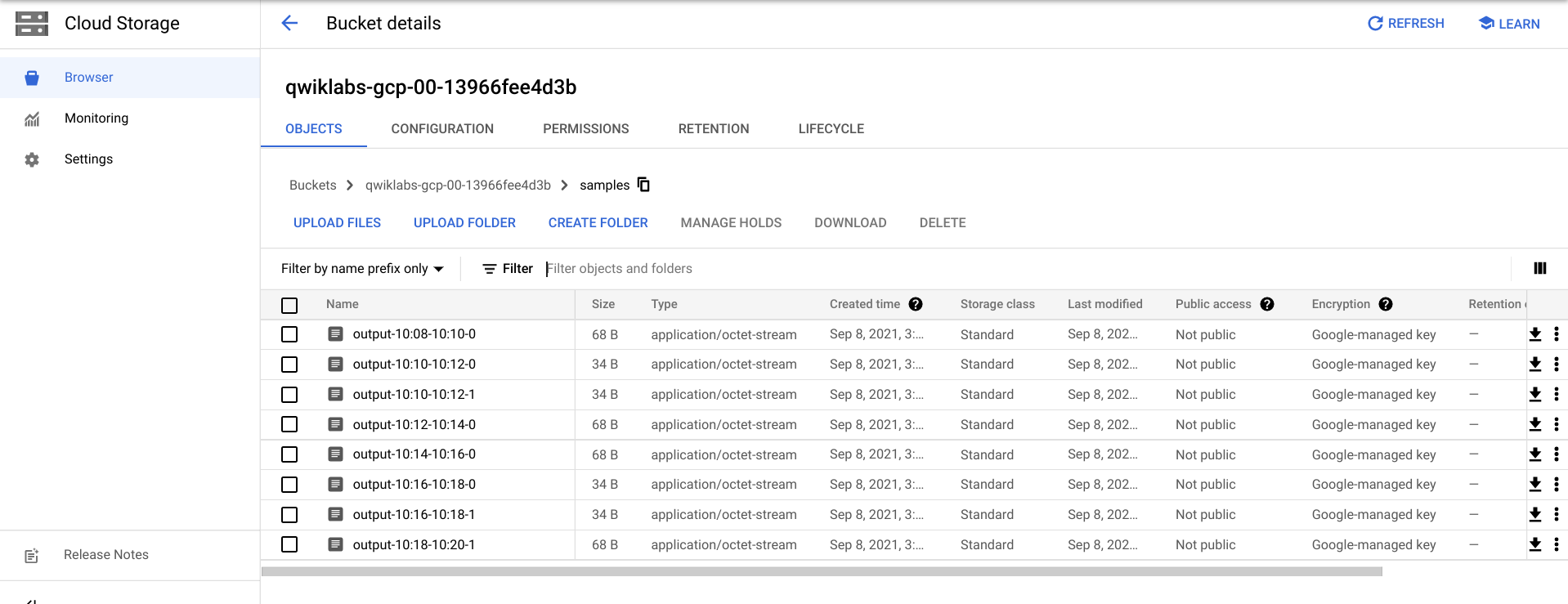
您可能需要等待几分钟,才能在 Cloud Storage 中看到输出文件。
- 如需查看输出文件,请前往导航菜单 > Cloud Storage,点击您的存储桶名称,然后点击 Samples。
- 或者,您可以使用 CTRL+C 退出在 Cloud Shell 中运行的应用(如果使用 Python 选项,请输入
exit),然后执行以下命令,列出已写入 Cloud Storage 的文件:
gsutil ls gs://${BUCKET_NAME}/samples/
输出应如下所示:
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:30-22:32-0-of-1
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:32-22:34-0-of-1
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:34-22:36-0-of-1
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:36-22:38-0-of-1
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:30-22:32-0
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:30-22:32-1
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:32-22:34-0
gs://{$BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output-22:32-22:34-1
任务 5. 清理
- 如果您尚未退出应用,请使用 CTRL+C 退出在 Cloud Shell 中运行的应用。
如果使用 Python 选项,请输入 exit 以退出 Python 环境。
- 在 Cloud Shell 中删除 Cloud Scheduler 作业:
gcloud scheduler jobs delete publisher-job
如果系统提示“Do you want to continue”,请按 Y 并按 Enter 键。
- 在 Dataflow 控制台中,选择您的作业名称,然后点击停止,以停止作业。
出现提示时,点击停止作业 > 取消,以取消流水线而不执行排空操作。
- 在 Cloud Shell 中删除主题:
gcloud pubsub topics delete $TOPIC_ID
- 在 Cloud Shell 中删除流水线创建的文件:
gsutil -m rm -rf "gs://${BUCKET_NAME}/samples/output*"
gsutil -m rm -rf "gs://${BUCKET_NAME}/temp/*"
- 在 Cloud Shell 中删除 Cloud Storage 存储桶:
gsutil rb gs://${BUCKET_NAME}
恭喜!
您成功创建了一个 Dataflow 流水线,该流水线从您的 Pub/Sub 主题读取消息,按时间戳对消息进行窗口化处理,并将其写入您的 Cloud Storage 存储桶。
后续步骤/了解详情
Google Cloud 培训和认证
…可帮助您充分利用 Google Cloud 技术。我们的课程会讲解各项技能与最佳实践,可帮助您迅速上手使用并继续学习更深入的知识。我们提供从基础到高级的全方位培训,并有点播、直播和虚拟三种方式选择,让您可以按照自己的日程安排学习时间。各项认证可以帮助您核实并证明您在 Google Cloud 技术方面的技能与专业知识。
上次更新手册的时间:2025 年 8 月 20 日
上次测试实验的时间:2025 年 8 月 20 日
版权所有 2026 Google LLC 保留所有权利。Google 和 Google 徽标是 Google LLC 的商标。其他所有公司名和产品名可能是其各自相关公司的商标。











