Overview
A Cloud Run function is a piece of code that runs in response to an event, such as an HTTP request, a message from a messaging service, or a file upload. Cloud events are things that happen in your cloud environment. These might be things like changes to data in a database, files added to a storage system, or a new virtual machine instance being created.
Since Cloud Run functions are event-driven, they only run when something happens. This makes them a good choice for tasks that need to be done quickly or that don't need to be running all the time.
This hands-on lab shows you how to create, deploy, and test a Cloud Run function which will load a BigQuery table using the Google Cloud SDK.
What you'll do
- Create a Cloud Run function
- Deploy and test the Cloud Run function
- View data in BigQuery and Cloud Run function logs
Setup and Requirements
For each lab, you get a new Google Cloud project and set of resources for a fixed time at no cost.
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method.
On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account.
-
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}}
You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}}
You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials.
Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges.
-
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.
Note: To view a menu with a list of Google Cloud products and services, click the Navigation menu at the top-left, or type the service or product name in the Search field.

Activate Google Cloud Shell
Google Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud.
Google Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
-
In Cloud console, on the top right toolbar, click the Open Cloud Shell button.
-
Click Continue.
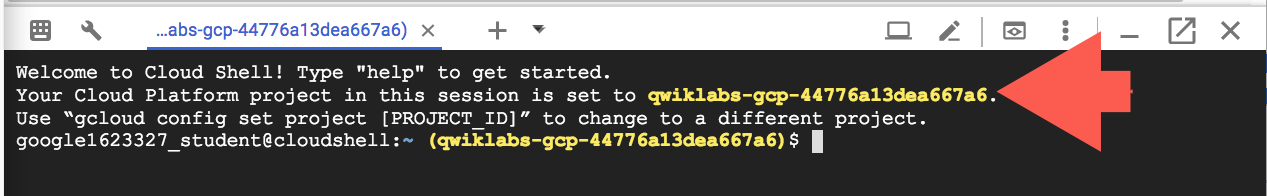
It takes a few moments to provision and connect to the environment. When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your PROJECT_ID. For example:
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
- You can list the active account name with this command:
gcloud auth list
Output:
Credentialed accounts:
- @.com (active)
Example output:
Credentialed accounts:
- google1623327_student@qwiklabs.net
- You can list the project ID with this command:
gcloud config list project
Output:
[core]
project =
Example output:
[core]
project = qwiklabs-gcp-44776a13dea667a6
Note:
Full documentation of gcloud is available in the
gcloud CLI overview guide
.
Task 1. Enable APIs
In this task, you enable the relevant APIs before you create the Cloud Run functions.
- In Cloud Shell, run the following command to set your Project ID variable:
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
- Run the following commands to set the Region variable:
export REGION={{{project_0.default_region | "REGION"}}}
gcloud config set compute/region $REGION
- Run the following commands to set the configuration variables:
gcloud config set run/region $REGION
gcloud config set run/platform managed
gcloud config set eventarc/location $REGION
- Run the following commands to enable all necessary services:
gcloud services enable \
artifactregistry.googleapis.com \
cloudfunctions.googleapis.com \
cloudbuild.googleapis.com \
eventarc.googleapis.com \
run.googleapis.com \
logging.googleapis.com \
pubsub.googleapis.com
Note: For Eventarc, It may take a few minutes before all of the permissions are propagated to the service agent
Task 2. Set required permissions
In this task, you grant the default Compute Engine service account the ability to receive Eventarc events, and the Cloud Storage service agent the permission to publish messages to Pub/Sub topics, enabling event-driven workflows and storage-triggered actions.
- In Cloud Shell, run the following command to set the PROJECT_NUMBER variable:
export PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format='value(projectNumber)')
- Run the following command to grant the default Compute Engine service account within your project the necessary permissions to receive events from Eventarc:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:$PROJECT_NUMBER-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/eventarc.eventReceiver"
- Run the following commands to retrieve the Cloud Storage service agent for your project, and grant it the permission to publish messages to Pub/Sub topics:
SERVICE_ACCOUNT="$(gcloud storage service-agent --project=$PROJECT_ID)"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}" \
--role='roles/pubsub.publisher'
Task 3. Create the function
In this task, you create a simple function named loadBigQueryFromAvro. This function reads an Avro file that is uploaded to Cloud Storage and then creates and loads a table in BigQuery.
- In Cloud Shell, run the following command to create and open a file named
index.js:
nano index.js
- Copy the following code for the Cloud Function into the
index.js file:
/**
* index.js Cloud Function - Avro on GCS to BQ
*/
const {Storage} = require('@google-cloud/storage');
const {BigQuery} = require('@google-cloud/bigquery');
const storage = new Storage();
const bigquery = new BigQuery();
exports.loadBigQueryFromAvro = async (event, context) => {
try {
// Check for valid event data and extract bucket name
if (!event || !event.bucket) {
throw new Error('Invalid event data. Missing bucket information.');
}
const bucketName = event.bucket;
const fileName = event.name;
// BigQuery configuration
const datasetId = 'loadavro';
const tableId = fileName.replace('.avro', '');
const options = {
sourceFormat: 'AVRO',
autodetect: true,
createDisposition: 'CREATE_IF_NEEDED',
writeDisposition: 'WRITE_TRUNCATE',
};
// Load job configuration
const loadJob = bigquery
.dataset(datasetId)
.table(tableId)
.load(storage.bucket(bucketName).file(fileName), options);
await loadJob;
console.log(`Job ${loadJob.id} completed. Created table ${tableId}.`);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error loading data into BigQuery:', error);
throw error;
}
};
- In nano press (Ctrl+x) , and then press (Y), and then press Enter to save the file.
Create a function.
Task 4. Create a Cloud Storage bucket and BigQuery dataset
In this task, you set up the background infrastructure to store assets used to invoke the Cloud Run function (a Cloud Storage bucket), and then store the output in BigQuery when it completes.
- In Cloud Shell, run the following command to create a new Cloud Storage bucket as a staging location:
gcloud storage buckets create gs://$PROJECT_ID --location=$REGION
- Run the following command to create a BQ dataset to store the data:
bq mk -d loadavro
Create a Cloud Storage bucket and BigQuery dataset.
Task 5. Deploy your function
In this task, you deploy the new Cloud Run function and trigger it so that the data is loaded into BigQuery.
- In Cloud Shell, run the following command to install the two javascript libraries to read from Cloud Storage and store the output in BigQuery:
npm install @google-cloud/storage @google-cloud/bigquery
- Run the following command to deploy the function:
gcloud functions deploy loadBigQueryFromAvro \
--gen2 \
--runtime nodejs20 \
--source . \
--region $REGION \
--trigger-resource gs://$PROJECT_ID \
--trigger-event google.storage.object.finalize \
--memory=512Mi \
--timeout=540s \
--service-account=$PROJECT_NUMBER-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com
Note: If you see an error message relating to eventarc service agent propagation, wait a few minutes and try the command again.
- Run the following command to confirm that the trigger was successfully created. The output will be similar to the following:
gcloud eventarc triggers list --location=$REGION
NAME: loadbigqueryfromavro-177311
TYPE: google.cloud.storage.object.v1.finalized
DESTINATION: Cloud Functions: loadBigQueryFromAvro
ACTIVE: Yes
LOCATION: europe-west1
- Run the following command to download the Avro file that will be processed by the Cloud Run function for storage in BigQuery:
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/cloud-training/dataengineering/lab_assets/idegc/campaigns.avro
- Run the following command to move the Avro file to the staging Cloud Storage bucket you created earlier. This action will trigger the Cloud Run function:
gcloud storage cp campaigns.avro gs://{{{project_0.project_id |PROJECT_ID}}}
Deploy a function.
Task 6. Confirm that the data was loaded into BigQuery
In this task, you confirm that the data processed by the Cloud Run function has been successfully loaded into BigQuery by querying the loadavro.campaigns table using the bq command
- In Cloud Shell, run the following command to view the data in the new table in BigQuery, using the bq command:
bq query \
--use_legacy_sql=false \
'SELECT * FROM `loadavro.campaigns`;'
Note: The Cloud Run function will typically process very quickly but it is possible the query run against BigQuery may not return results. If that is the case for you please wait a moment and run the query again.
The query should return results similar to the following:
Example output:
+------------+--------+---------------------+--------+---------------------+----------+-----+
| created_at | period | campaign_name | amount | advertising_channel | bid_type | id |
+------------+--------+---------------------+--------+---------------------+----------+-----+
| 2020-09-17 | 90 | NA - Video - Other | 41 | Video | CPC | 81 |
| 2021-01-19 | 30 | NA - Video - Promo | 325 | Video | CPC | 137 |
| 2021-06-28 | 30 | NA - Video - Promo | 78 | Video | CPC | 214 |
| 2021-03-15 | 30 | EU - Search - Brand | 465 | Search | CPC | 170 |
| 2022-01-01 | 30 | EU - Search - Brand | 83 | Search | CPC | 276 |
| 2020-02-18 | 30 | EU - Search - Brand | 30 | Search | CPC | 25 |
| 2021-06-08 | 30 | EU - Search - Brand | 172 | Search | CPC | 201 |
| 2020-11-29 | 60 | EU - Search - Other | 83 | Search | CPC | 115 |
| 2021-09-11 | 30 | EU - Search - Other | 86 | Search | CPC | 237 |
| 2022-02-17 | 30 | EU - Search - Other | 64 | Search | CPC | 296 |
+------------+--------+---------------------+--------+---------------------+----------+-----+
Task 7. View logs
In this task, you retrieve all log entries that are associated with your service named loadBigQueryFromAvro.
- In Cloud Shell, run the following command to examine the logs for your Cloud Run function:
gcloud logging read "resource.labels.service_name=loadBigQueryFromAvro"
Messages in the log appear similar to the following:
resource:
labels:
configuration_name: loadbigqueryfromavro
location: europe-west1
project_id: qwiklabs-gcp-04-16fde64676e4
revision_name: loadbigqueryfromavro-00001-wim
service_name: loadbigqueryfromavro
type: cloud_run_revision
spanId: '5804952652695382607'
textPayload: |
Job undefined completed. Created table campaigns.
timestamp: '2025-03-10T17:24:43.560594Z'
Congratulations!
You used the Google Cloud SDK to create, deploy, and test a Cloud Run function that created and loaded a BigQuery table.
Copyright 2025 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.










